Solid-state Batteries
The solid-state batteries are expected to be the next-generation energy storage technology, which can directly use charge carrier metal as the anode, providing much higher energy density than current lithium-ion batteries. Among different components of solid-state batteries, the conductive filler-based solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs) show great importance to achieve large-scale applications. However, the transport and conduction mechanisms of lithium-ion (Li+) in such SPEs remain unclear. Inadequate understading of complex interrelationships in multiple components, including polymer matrix, lithium salt, filler, and additive, limits device versatility and improvement. In addition, the design of a ploymer-based separator with excellent volume-responsive function is found effective to supppress the growth of lithium dendrites , thus increasing the charging and discharging densities.
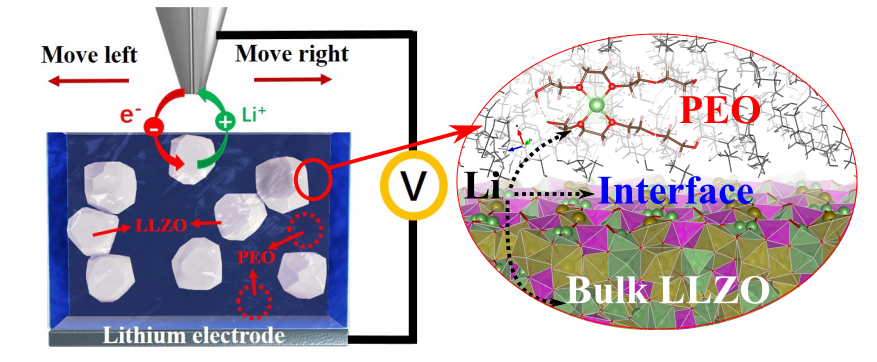
Keywords: Membrane; Suppression of Lithium Dendrites; Solid-state Electrolytes (LLZO, etc) ; Li+ Transport Mechanism
Publications:
Chuan Shi, Jianjun Song, Yang Zhang, Xiuting Wang, Zhen Jiang*, Tong Sun*, and Jinbao Zhao Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 4, 101321 (2023) (*: corresponding authors) [DOI]
Chuan Shi, Lei Zhang, Xiu Ting, Tong Sun*, Zhen Jiang*, and Jinbao Zhao* ACS. Appl. Mater. Interface 14, 51931-51940 (2022) (*: corresponding authors) [DOI]
